How can brain scans help treat and prevent PTSD?
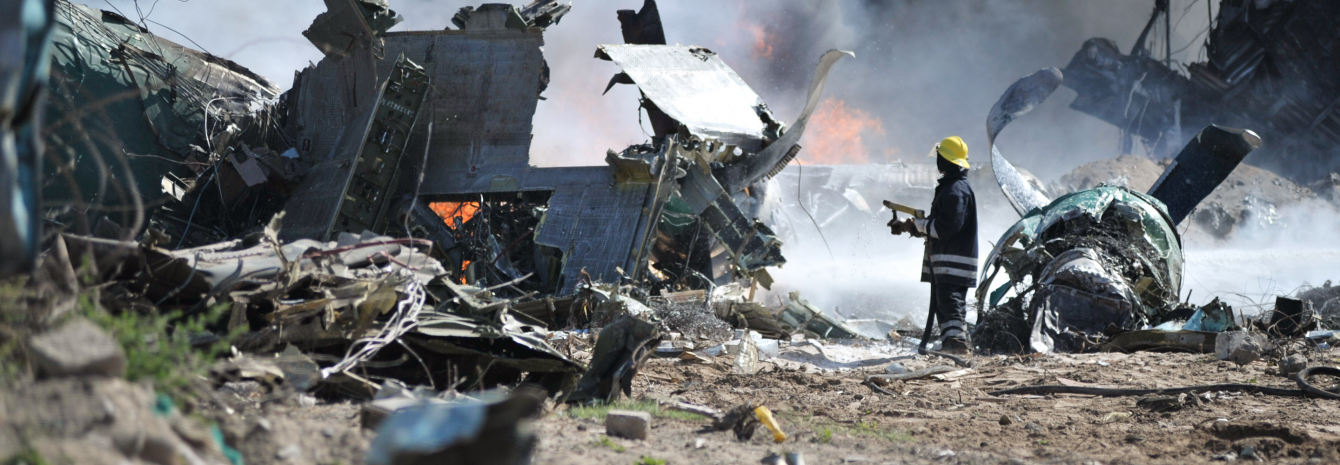

Yuval Neria, professor of medical psychology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center and Columbia's Mailman School of Public Health, and his colleagues discovered a link between hippocampus size and treatment response for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The hippocampus is a brain area that distinguishes between safety and danger, and prior research has shown a smaller hippocampus elevates the risk of having PTSD. These findings impact those engaged in potentially traumatic activities.
“For example, new recruits for military service may be scanned before an assignment to determine whether they are capable of dealing with the expected stress and trauma,” said Neria.
The most recent study Neria and his colleagues conducted focused on hippocampus size and PTSD treatment effectiveness, showing a larger hippocampus increases the likelihood of a positive response to treatment. This study not only strengthens theories that the hippocampus plays a large role in PTSD, but also points to new methods of screening for the disorder and tailoring treatment to the individual. Learn more.
Make Your Commitment Today